How to Ease Thoracic Disc Herniation Pain- Innovative Health
Thoracic disc herniation occurs when the gel-like center of a disc in the thoracic spine pushes through a tear in the outer layer, causing pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This condition can lead to various symptoms, including back pain, muscle weakness, and numbness. Understanding the causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management.
Diagnosis and Understanding
Diagnosing thoracic disc herniation typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. Understanding the anatomy of the thoracic spine helps in identifying the location and severity of the herniation. This process begins with gathering detailed information about the patient’s medical background, including any symptoms experienced and previous injuries or conditions.
A thorough physical examination follows, during which a healthcare provider assesses the patient’s range of motion, reflexes, and any signs of nerve compression or spinal instability. Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans are then utilized to visualize the internal structures of the thoracic spine, allowing for a precise diagnosis of disc herniation and guiding treatment decisions.
Tips for Managing Pain
Pain management is crucial in addressing thoracic disc herniation, a condition characterized by discomfort and limitation. Non-surgical approaches, like ice and heat therapy along with over-the-counter medications, offer avenues for relief. Moreover, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining proper posture and optimizing workspace ergonomics contribute significantly to pain alleviation. These combined strategies form an integral part of managing thoracic disc herniation effectively, aiming to enhance comfort and functionality for individuals experiencing this condition.
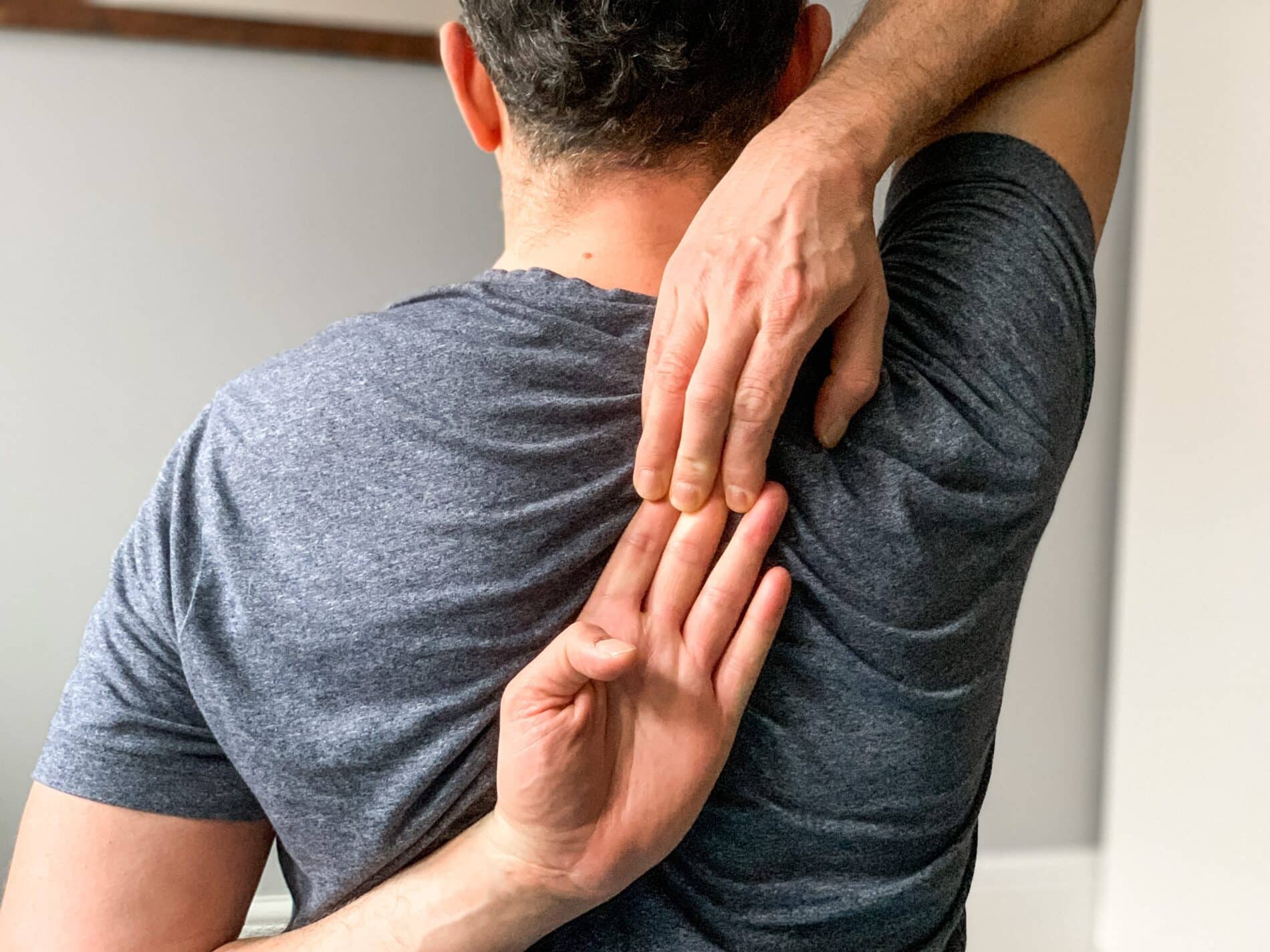
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy plays a vital role in improving mobility and reducing pain associated with thoracic disc herniation. This specialized form of therapy involves targeted interventions to address the unique challenges posed by thoracic disc herniation. A key component of the rehabilitation process includes strengthening exercises that specifically target the core and back muscles. By focusing on these muscle groups, physical therapists aim to enhance spinal stability and promote better support for the thoracic region.
Additionally, flexibility exercises are incorporated into the treatment plan to improve the range of motion in the affected area, further contributing to overall recovery. The combination of strengthening and flexibility exercises not only aids in alleviating existing symptoms but also plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of future injuries or complications.
Through a comprehensive approach, physical therapy empowers individuals with thoracic disc herniation to regain function, minimize discomfort, and optimize their long-term spinal health.
Medication and Injections
In certain situations, healthcare providers may recommend the use of medications to address pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants are examples of such medications that may be prescribed for effective pain management. Additionally, healthcare professionals might consider administering epidural steroid injections as part of the treatment plan.
These injections can offer temporary relief by reducing inflammation in the vicinity of the affected nerves. This multifaceted approach aims to address both pain and inflammation, providing patients with a more comprehensive strategy for managing their symptoms.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy can complement conventional treatments for thoracic disc herniation. These therapies may help alleviate pain, improve flexibility, and promote overall well-being.
Surgical Options
Surgery may be recommended for severe cases of thoracic disc herniation that do not respond to conservative treatments. Common surgical procedures include discectomy, laminectomy, and spinal fusion, aimed at decompressing the spinal cord and stabilizing the spine.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after surgery involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and rehabilitation exercises. Following a structured rehabilitation program helps restore strength, flexibility, and function to the spine, enabling a quicker return to normal activities.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing thoracic disc herniation involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, proper lifting techniques, and avoiding smoking. Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace and using supportive devices can also reduce the risk of spinal injuries.
Importance of Proper Posture
Maintaining good posture is essential for spinal health, especially for individuals with thoracic disc herniation. Practicing proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting objects reduces strain on the spine and minimizes the risk of exacerbating existing symptoms.
Nutrition and Supplements
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall spinal health and can aid in the healing process. Supplements such as calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids may help strengthen bones and reduce inflammation in the spine.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate pain and discomfort associated with thoracic disc herniation. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Supportive Devices
Using supportive devices such as braces, lumbar cushions, and ergonomic chairs can provide additional support and comfort for individuals with thoracic disc herniation. These devices help maintain proper spinal alignment and reduce pressure on the affected area.
Seeking Professional Help
It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment of thoracic disc herniation. Specialists such as orthopedic surgeons, neurologists, and physical therapists can offer personalized care and guidance based on individual needs.
Conclusion
Thoracic disc herniation can cause significant pain and discomfort, but with proper management strategies, individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. By incorporating a combination of conservative treatments, alternative therapies, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and prevent further complications.
FAQs
How common is thoracic disc herniation?
Thoracic disc herniation is less common than herniations in the lumbar or cervical spine but can still occur, particularly due to trauma or degenerative changes.
Can thoracic disc herniation cause symptoms in other parts of the body?
Yes, thoracic disc herniation can cause symptoms such as radiating pain, numbness, or weakness in the chest, abdomen, or limbs, depending on the location of the herniation.
Is surgery always necessary for thoracic disc herniation?
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there are severe neurological symptoms such as paralysis or loss of bowel/bladder control.
How long does recovery take after surgery for thoracic disc herniation?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery performed and individual factors. It may take several weeks to months to fully recover and return to normal activities.
Are there any long-term complications of thoracic disc herniation?
In some cases, thoracic disc herniation can lead to chronic pain, nerve damage, or spinal cord compression if left untreated. Seeking timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent complications.


