Avoiding Inflammations: Best Guides from Innovative Health
Inflammation, while a natural response by the body to protect against infection and injury, can become problematic when it persists for long periods. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. In this article, we’ll explore innovative approaches to avoiding inflammations and promoting overall well-being.
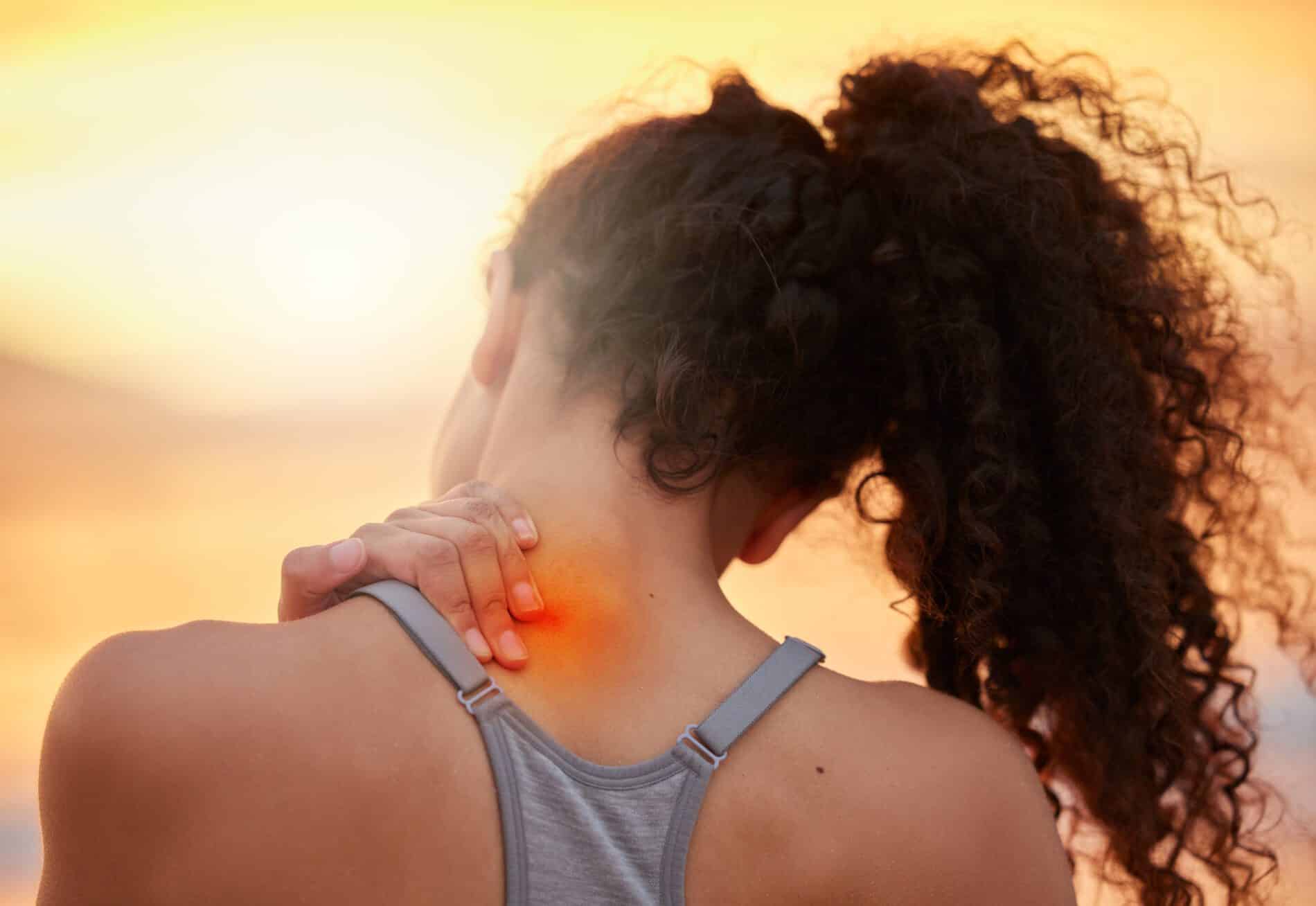
Avoiding Inflammations: Best Guides from Innovative Health
The processes underlying pain and its sensitization primarily occur within the brain. Peripheral nerves, specifically type III and type IV nerve fibers, transmit pain signals. These fibers connect through glial cells in various layers of the spinal cord, including laminae II, IV, V, and VI. From there, the pain signal travels via the spinothalamic tract to the thalamus, where the limbic system processes and stores the information.
Type IV fibers, responsible for initiating the synaptic cascade to the brain, also convey sensations of their own. When activated, they release substances like Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) and substance P, triggering an inflammatory response. This response activates immune cells such as macrophages, mast cells, and endothelial cells, which enact protective mechanisms in the body. However, excessive activation of type IV fibers can lead to frequent calls for these inflammatory mediators, resulting in widespread inflammation.
What are inflammations?
Inflammation is the body’s response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It is characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain in the affected area.
Why are they harmful?
While acute inflammation is necessary for healing, chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
Understanding Inflammation
Types of inflammation
Inflammation can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation occurs rapidly and is typically resolved within a few days. Chronic inflammation persists over time and can lead to long-term health problems.
Causes of inflammation
Various factors can trigger inflammation, including infections, injuries, autoimmune disorders, unhealthy diet, stress, and environmental toxins.
Impact of Inflammation on Health
Chronic diseases associated with inflammation
Chronic inflammation has been linked to conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and arthritis.
Effects on overall well-being
In addition to physical health issues, chronic inflammation can also affect mental well-being, leading to mood disorders and cognitive decline.
Innovative Approaches to Avoid Inflammation
Dietary strategies
Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle changes
Making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight can lower inflammation levels.
Supplements and herbs
Certain supplements and herbs, such as omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties and can be beneficial in managing inflammation.
Holistic Health Practices
Mind-body connection
Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce inflammation by promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
Stress management techniques
Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation. Implementing stress management techniques such as mindfulness and spending time in nature can help mitigate its effects.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Importance of regular exercise
Regular physical activity helps reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and boost overall health.
Types of exercises beneficial for inflammations
Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are gentle on the joints and can help alleviate inflammation.
Quality Sleep
Relationship between sleep and inflammations
Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep can lead to increased inflammation levels in the body.
Tips for improving sleep quality
Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment can promote better sleep and reduce inflammation.
Hydration and its Role
Importance of staying hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal bodily functions and reducing inflammation.
Best hydration practices
Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day and consuming hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables can support hydration levels.
Environmental Factors
Toxins and pollutants contributing to inflammations
Exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants, such as air pollution and chemicals in household products, can increase inflammations in the body.
Ways to minimize exposure
Taking steps to reduce exposure to toxins, such as using natural cleaning products, and air purifiers, and avoiding cigarette smoke, can help lower inflammation levels.
Mindfulness and Mental Well-being
Practices for reducing mental stress
Incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation, journaling, and spending time in nature can help reduce stress and inflammation.
Techniques for promoting mental clarity
Engaging in activities that promote mental clarity, such as reading, puzzles, and creative hobbies, can enhance cognitive function and reduce inflammation.
Healthy Eating Habits
Anti-inflammatory foods
Including foods like berries, leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish in your diet can help combat inflammation and support overall health.
Foods to avoid
Limiting intake of processed foods, refined sugars, trans fats, and excessive alcohol can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Supplements for Inflammation
Evidence-based supplements
Certain supplements, such as fish oil, curcumin, and probiotics, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help manage inflammations.
Dosage and precautions
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure safety.
Herbal Remedies
Popular herbs for reducing inflammations
Herbs like turmeric, ginger, green tea, and garlic have potent anti-inflammatory properties and can be incorporated into daily meals or taken as supplements.
Incorporating herbs into daily routine
Adding herbs to soups, salads, and smoothies, or brewing them into teas can provide a flavorful way to reap their anti-inflammatory benefits.
Innovative Technologies
Role of technology in inflammations management
Advancements in technology have led to the development of apps, wearables, and devices that can track various health markers related to inflammation.
Apps and devices for tracking health markers
Tools like fitness trackers, sleep monitors, and inflammation-tracking apps can help individuals monitor their health and make informed decisions about lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Inflammations is a natural process in the body, but chronic inflammation can have detrimental effects on health. By adopting innovative approaches such as dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, and incorporating anti-inflammatory supplements and herbs, individuals can reduce inflammation levels and promote overall well-being.
FAQs
What are the main causes of inflammation?
Inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including infections, injuries, unhealthy diet, stress, and environmental toxins.
How does stress contribute to inflammation?
Chronic stress can activate the body’s inflammatory response, leading to increased inflammation levels over time.
Are there any natural remedies for reducing inflammation?
Yes, several herbs and supplements have anti-inflammatory properties, including turmeric, ginger, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce inflammation?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, proper nutrition, stress management, and adequate sleep can help lower inflammation levels.
When should I consult a healthcare professional about inflammations?
If you experience persistent inflammation symptoms or have concerns about your health, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.


